Table of Contents OOPs concepts in Java
- What is an Object
- What is a class
- Constructor in Java
- Object Oriented Programming Features
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstract Class and Methods
- Interfaces in Java
What is an Object OOPs concept in Java

Object: is a collection of data and its behavior (known as methods).
Objects have two characteristics:
- states
- behaviors.
states and behaviors Examples are given below
Example 1:
Object: House
State: Address, Color, Rooms, stories
Behavior: Open gate, close gate
class House {
String address;
String color;
integer Rooms;
integer Stories;
double are;
void openDoor() {
// code
}
void closeDoor() {
// code
}
...
...
}Example 2:
In this example, we take a car as an object
Object: Car
State: Color, Brand, Model, Weight
Behavior: Break, Accelerate, Gear change, Slow Down.
Note: As we know that the behaviors of an object, can be represented by variables and methods in the related class.
Characteristics of Objects:
There are three main characteristics of Objects these are:
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Message Passing
Abstraction: Abstraction is a process that shows only “relevant” data and “hides” unnecessary details of an object.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation simply means binding object states (fields) and behavior (methods) together. If we are creating a class, it means that we are doing encapsulation.
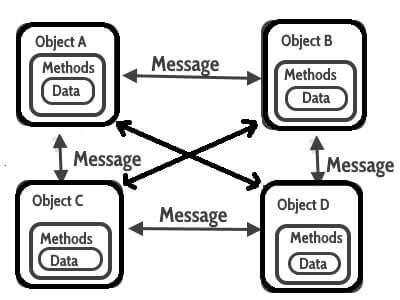
Message Passing
Message passing in Java means sending an object i.e. message from one thread to another thread. An application may have many objects and a single object in nothing if it does not interact with other objects. So, one object interacts with another object by invoking methods on that object. It is also called Method Invocation.
Method Invocation is used when threads do not have shared memory
Class in OOPs
Classes, In object-oriented programming, a class is considered a blueprint for creating objects (a particular data structure), providing initial values for state (member variables or attributes), and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods). The class is a blueprint that defines the nature of a future object.
